draw the major organic product formed in the reaction. Embark on a scientific expedition into the realm of organic chemistry, where we unravel the intricacies of predicting the major organic products formed in reactions. Join us as we delve into the depths of reaction mechanisms, regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and experimental conditions, deciphering the factors that govern the outcome of organic transformations.
Our journey begins with a thorough examination of the concept of a major organic product, laying the foundation for understanding how various factors influence its formation. We will then explore the diverse reaction mechanisms that orchestrate organic transformations, demonstrating their significance in predicting the major organic product.
Major Organic Product Identification
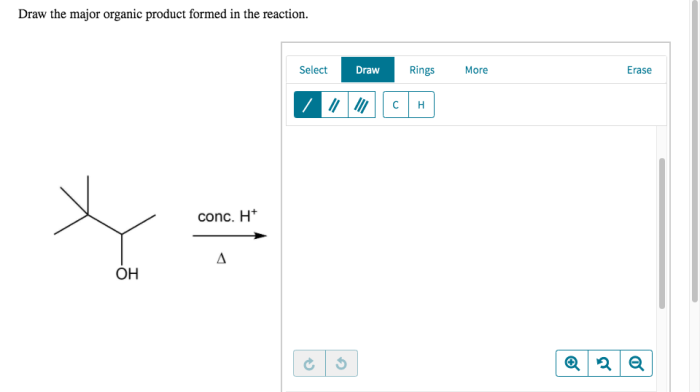
In organic chemistry, the major organic product is the predominant product formed in a reaction. Its formation is influenced by several factors, including the stability of the product, the reaction mechanism, and the experimental conditions.
Factors Influencing Major Organic Product Formation
- Stability of the product:More stable products are more likely to form as they are lower in energy.
- Reaction mechanism:The mechanism of a reaction determines the pathway by which the product is formed, influencing its regioselectivity and stereoselectivity.
- Experimental conditions:Factors such as temperature, solvent, and catalysts can affect the reaction pathway and product distribution.
Examples of Reactions and Major Organic Products, Draw the major organic product formed in the reaction.
| Reaction | Major Organic Product |
|---|---|
| Electrophilic aromatic substitution (EAS) | Substituted benzene |
| Nucleophilic addition to carbonyl compounds | Alcohol or amine |
| Diels-Alder reaction | Cyclohexene |
Reaction Mechanisms

Reaction mechanisms describe the stepwise sequence of events that lead to the formation of a product. Understanding reaction mechanisms is crucial for predicting the major organic product.
Types of Reaction Mechanisms
- Nucleophilic substitution:SN1, SN2, SNAr
- Electrophilic addition:Markovnikov’s rule, anti-Markovnikov’s rule
- Elimination:E1, E2, E1cB
- Radical reactions:Homolytic bond cleavage, radical recombination
Reaction Mechanisms and Major Organic Products
| Mechanism | Major Organic Product |
|---|---|
| SN2 | Substituted product |
| SN1 | Alkyl halide or carbocation |
| E2 | Zaitsev’s product |
| Radical addition | Alkyl radical |
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity: Draw The Major Organic Product Formed In The Reaction.
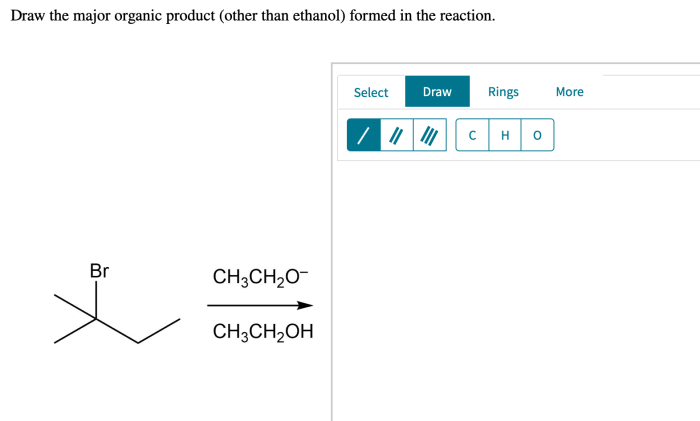
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity are important concepts in organic chemistry that influence the formation of the major organic product.
Regioselectivity
Regioselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to occur at a specific site within a molecule. It is influenced by factors such as the stability of the carbocation or radical intermediate.
Stereoselectivity
Stereoselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to produce a specific stereoisomer. It is influenced by factors such as the steric hindrance and the electronic effects of the reactants.
Impact of Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity on Product Outcomes
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity can significantly impact the product outcomes of a reaction. By understanding these concepts, chemists can design reactions to selectively produce desired products.
Experimental Conditions
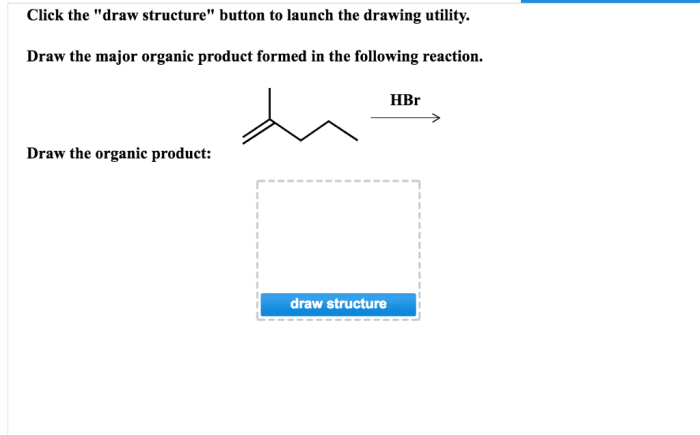
Experimental conditions play a crucial role in determining the major organic product. Factors such as temperature, solvent, and catalysts can influence the reaction pathway and product distribution.
Temperature
Temperature affects the reaction rate and the equilibrium position. Higher temperatures generally favor reactions that lead to more stable products.
Solvent
The solvent can affect the solubility of the reactants and products, as well as the polarity of the reaction environment. Polar solvents favor ionic reactions, while nonpolar solvents favor nonpolar reactions.
Catalysts
Catalysts are substances that increase the reaction rate without being consumed. They can alter the reaction pathway and influence the formation of the major organic product.
Table of Experimental Conditions and Major Organic Product Formation
| Condition | Effect on Major Organic Product |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Higher temperatures favor more stable products |
| Solvent | Polar solvents favor ionic reactions, nonpolar solvents favor nonpolar reactions |
| Catalysts | Can alter the reaction pathway and influence product formation |
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of predicting major organic products?
Predicting major organic products is crucial in organic chemistry as it enables chemists to design efficient synthetic strategies, optimize reaction conditions, and minimize waste. It also facilitates the understanding of reaction mechanisms and the development of new methodologies.
How do reaction mechanisms influence the formation of major organic products?
Reaction mechanisms provide a detailed understanding of the step-by-step transformations that occur during a chemical reaction. By elucidating the reaction pathway, chemists can identify the key intermediates and transition states, which in turn helps predict the major organic product.
What is the role of regioselectivity and stereoselectivity in determining major organic products?
Regioselectivity and stereoselectivity control the regiochemical and stereochemical outcome of reactions, respectively. Regioselectivity dictates the position of functional group substitution, while stereoselectivity governs the spatial arrangement of atoms or groups within the molecule. Understanding these concepts is essential for predicting the major organic product.