Exercise 16 human reflex physiology – Exercise 16: Human Reflex Physiology embarks on an illuminating journey into the intricate workings of the human nervous system, unraveling the fascinating mechanisms that govern our reflexes. From defining the very essence of reflex physiology to exploring the diverse types of reflexes and their intricate neural pathways, this comprehensive guide delves into the profound impact of exercise on reflex physiology, highlighting its benefits and potential risks.
As we delve deeper, we uncover the remarkable clinical applications of reflex physiology, examining its invaluable role in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders. The future of reflex physiology research holds immense promise, with ongoing advancements shaping our understanding of human health and paving the way for groundbreaking therapeutic interventions.
Reflex Physiology
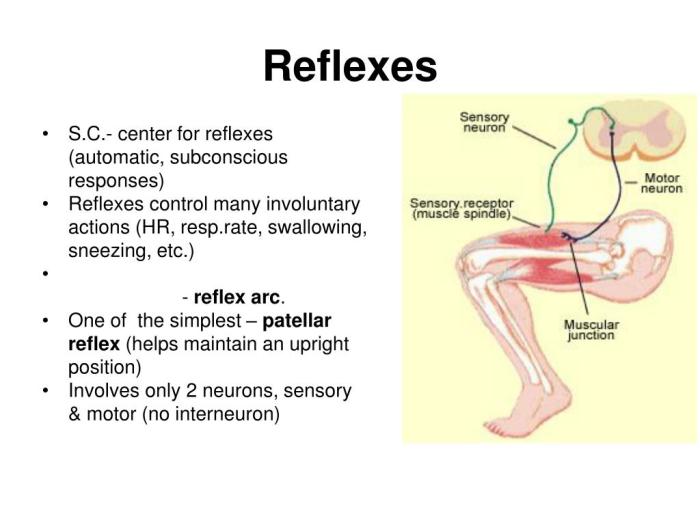
Reflex physiology encompasses the study of involuntary, rapid responses to stimuli that occur via neural pathways involving the spinal cord or brainstem without conscious control. These responses, known as reflexes, are essential for maintaining homeostasis, protecting the body from harm, and facilitating coordinated movement.
Types of Reflexes
- Somatic reflexesinvolve skeletal muscle responses to stimuli affecting the body’s surface or muscles.
- Autonomic reflexesregulate involuntary functions of the internal organs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
Neural Pathways Involved in Reflexes
Reflex arcs consist of five essential components:
- Receptor: Sensory receptor that detects the stimulus.
- Afferent neuron: Conducts sensory information from the receptor to the spinal cord or brainstem.
- Integration center: Spinal cord or brainstem where the sensory information is processed and an appropriate response is determined.
- Efferent neuron: Transmits the motor response from the integration center to the effector organ.
- Effector organ: Muscle or gland that executes the reflex response.
Exercise and Reflex Physiology

Exercise can significantly affect reflex physiology, both acutely and chronically. Acutely, exercise can increase the excitability of reflexes, such as the stretch reflex, which helps to protect the muscles from injury. Chronically, exercise can lead to changes in the structure and function of the nervous system, which can improve reflex performance.
Benefits of Exercise for Reflex Physiology
- Increased reflex excitability
- Improved reflex coordination
- Reduced risk of reflex-related injuries
Risks Associated with Exercise and Reflex Physiology, Exercise 16 human reflex physiology
While exercise is generally beneficial for reflex physiology, there are some risks associated with overexertion or improper technique.
- Overexertion can lead to muscle fatigue, which can impair reflex function.
- Improper technique can put excessive stress on the joints and muscles, which can lead to injury.
Clinical Applications of Reflex Physiology: Exercise 16 Human Reflex Physiology
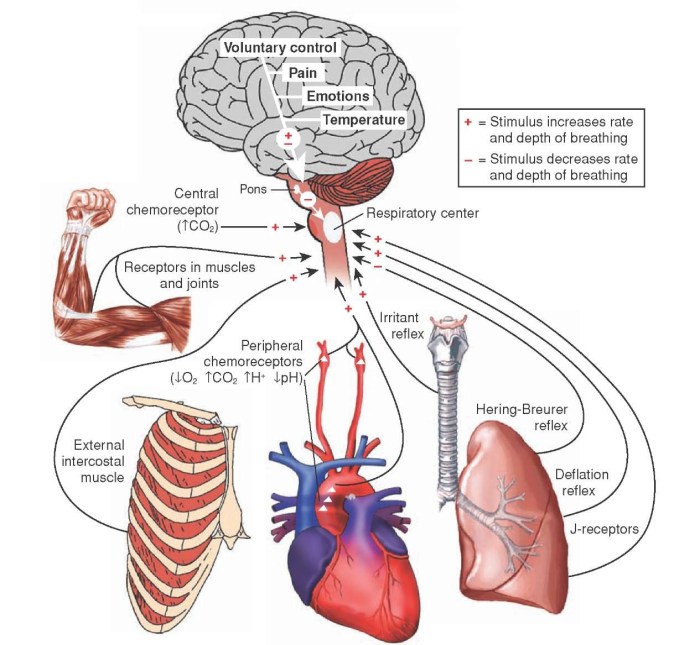
Reflex physiology plays a crucial role in clinical practice, providing valuable insights into the functioning of the nervous system. It aids in diagnosing and treating neurological disorders, assessing nerve damage, and evaluating the integrity of the spinal cord.
Reflex Testing
Reflex testing is a non-invasive technique used to evaluate the function of specific reflexes. Common reflex tests include:
- Patellar reflex (knee-jerk reflex):Tests the L4 and L5 spinal nerve roots, assessing the integrity of the quadriceps pathway.
- Achilles reflex (ankle jerk reflex):Tests the S1 and S2 spinal nerve roots, evaluating the gastrocnemius and soleus pathway.
- Biceps reflex:Tests the C5 and C6 spinal nerve roots, assessing the biceps pathway.
- Triceps reflex:Tests the C7 and C8 spinal nerve roots, evaluating the triceps pathway.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurological Disorders
Reflex physiology helps diagnose and treat various neurological disorders, including:
- Spinal cord injuries:Reflex testing can identify the level of spinal cord damage by assessing the function of reflexes below the injury site.
- Peripheral nerve damage:Reflex testing can determine the location and severity of nerve damage by assessing the response of specific reflexes.
- Neuromuscular disorders:Reflex physiology can help differentiate between upper and lower motor neuron lesions by evaluating the presence and nature of reflexes.
Future Directions in Reflex Physiology Research

Reflex physiology research is a rapidly growing field with the potential to improve our understanding of human health and disease. Current trends in reflex physiology research include the use of new technologies to study reflexes, the development of new animal models of reflex disorders, and the investigation of the role of reflexes in human health and disease.
Future directions for reflex physiology research include the development of new therapies for reflex disorders, the use of reflexes to improve human performance, and the development of new technologies to study reflexes. Reflex physiology research has the potential to lead to new treatments for a variety of conditions, including spinal cord injuries, stroke, and Parkinson’s disease.
How can reflex physiology research be used to improve human health?
Reflex physiology research can be used to improve human health in a number of ways. For example, reflex physiology research can be used to develop new treatments for reflex disorders. Reflex disorders are a group of conditions that affect the way that reflexes work.
These disorders can cause a variety of symptoms, including muscle weakness, spasticity, and pain. Reflex physiology research can also be used to develop new ways to improve human performance. For example, reflex physiology research can be used to develop new training methods for athletes that can help them to improve their speed, strength, and agility.
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of reflex physiology in understanding human movement?
Reflex physiology provides essential insights into the coordination and control of voluntary and involuntary movements, enabling us to comprehend the intricate interplay between the nervous system and musculoskeletal system.
How does exercise influence reflex physiology?
Exercise exerts a profound impact on reflex physiology, enhancing reflex sensitivity, reducing reflex latency, and modulating the overall responsiveness of the nervous system.
What are the potential risks associated with exercise and reflex physiology?
While exercise generally benefits reflex physiology, excessive or inappropriate exercise can lead to reflex dysfunction, muscle imbalances, and increased risk of injuries.