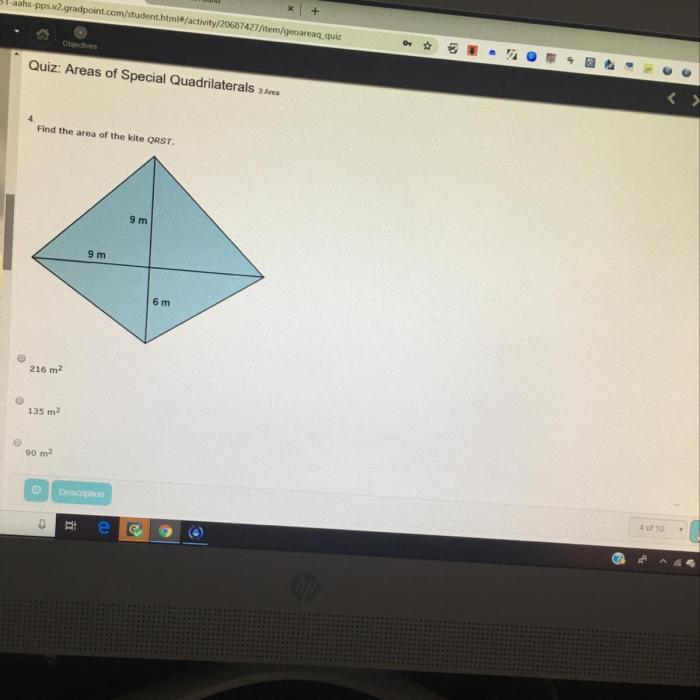
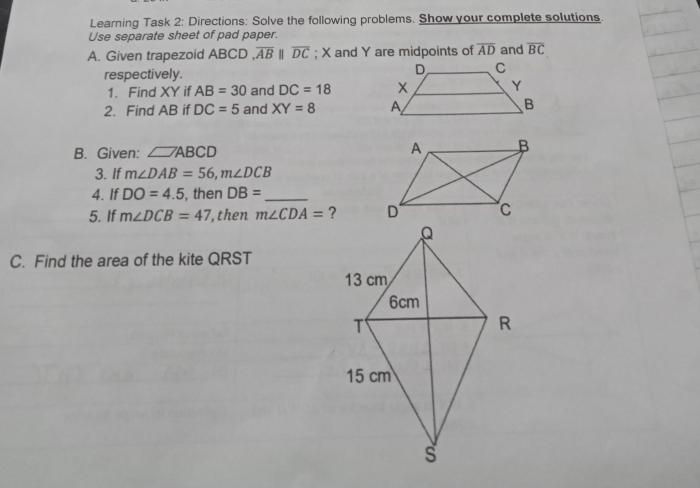
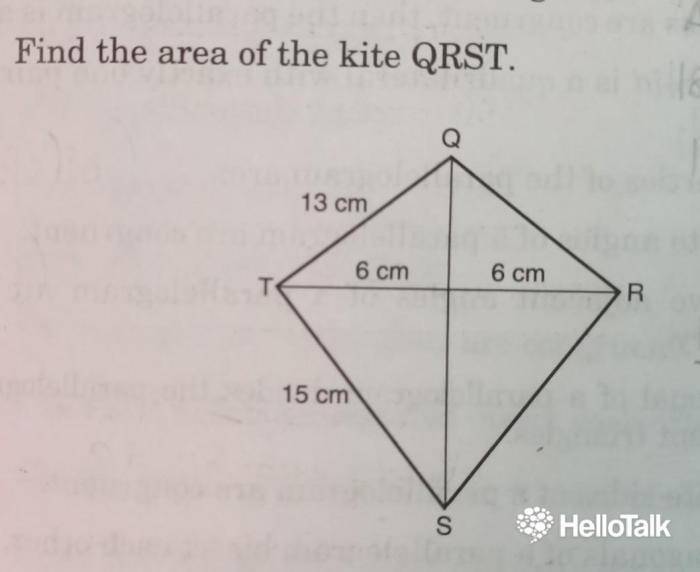
Find the area of the kite qrst – Delve into the fascinating world of geometry as we embark on a journey to find the area of Kite QRST. Join us as we explore the unique properties of kites, unravel the secrets of diagonals, and master the art of calculating their area with precision.
From understanding the basics to applying advanced techniques, this guide will equip you with all the knowledge you need to conquer the challenge of finding the area of any kite, no matter how complex.
Understanding the Concept of a Kite
A kite is a two-dimensional shape with four straight sides and two pairs of congruent adjacent sides. It is formed by two intersecting line segments that are not perpendicular to each other. The point of intersection is called the vertex, and the line segments that form the sides of the kite are called the arms.The
diagonals of a kite are the line segments that connect the opposite vertices. They intersect at a point called the centroid, which is the center of the kite. The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular to each other, and they bisect each other.
Calculating the Area of a Kite
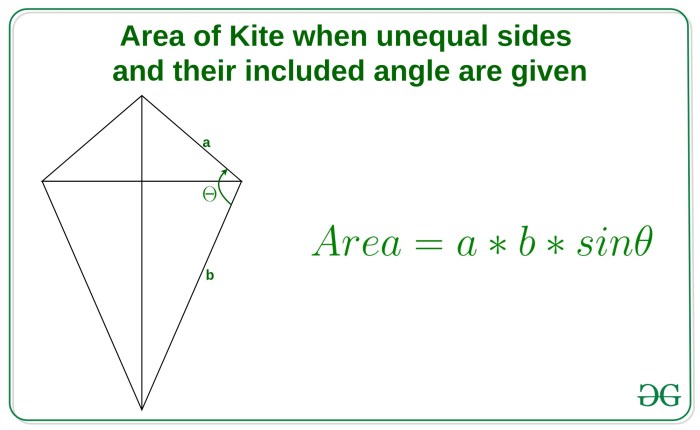
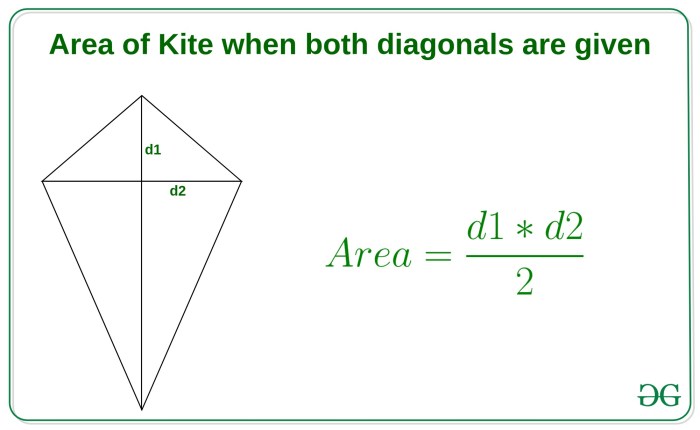
The area of a kite can be calculated using the formula:
Area = (1/2)
- (d1)
- (d2)
where:
- d1 is the length of one diagonal
- d2 is the length of the other diagonal
To apply this formula, follow these steps:
- Measure the lengths of both diagonals.
- Multiply the lengths of the diagonals together.
- Divide the product by 2.
- The result is the area of the kite.
Determining the Diagonals of a Kite
Determining the diagonals of a kite is crucial for calculating its area. There are two primary methods for finding the diagonals:
-*Using the Pythagorean Theorem
Divide the kite into two right triangles by drawing a line from one vertex to the opposite side.
To ace your upcoming AP Gov exam, check out the comprehensive ap gov ultimate review packet . It’s packed with essential materials to help you conquer any questions on the test. Once you’ve mastered the concepts, return to the task at hand: finding the area of the kite QRST.
- Label the sides of each triangle and use the Pythagorean theorem to find the lengths of the diagonals.
-*Using Geometric Relationships
Utilize the fact that the diagonals of a kite intersect at right angles.
Label the intersection point as O and the vertices as A, B, C, and D.
Use the properties of similar triangles to establish relationships between the sides and diagonals.
Using the Pythagorean Theorem
Let’s consider a kite with vertices A, B, C, and D. Draw a line from vertex A to side CD, intersecting at point E.
In triangle ABE, we have
AB = AC (kite diagonals are equal)
AE = 1/2(CD) (diagonal divides opposite side in half)
BE = 1/2(BC) (diagonal divides adjacent side in half)
Using the Pythagorean theorem
AB^2 = AE^2 + BE^2
(1/2 CD)^2 + (1/2 BC)^2 = AC^2
Solving for AC (diagonal length)
AC^2 = (1/4 CD^2) + (1/4 BC^2)
AC = √[(1/4 CD^2) + (1/4 BC^2)]
Applying the Area Formula: Find The Area Of The Kite Qrst
Now that we understand the formula for finding the area of a kite, let’s explore how to use it effectively.
The formula states that the area of a kite is half the product of its diagonals. That is, Area = (1/2)- d1 – d2 , where d1 and d2 represent the lengths of the diagonals.
Illustrative Examples, Find the area of the kite qrst
To illustrate the application of the formula, let’s consider a few examples:
- Example 1:Suppose we have a kite with diagonals measuring 10 cm and 12 cm. Using the formula, we can calculate its area as follows:
Area = (1/2)
- d1
- d2 = (1/2)
- 10 cm
- 12 cm = 60 cm2
- Example 2:Now, let’s consider a kite with diagonals of 15 cm and 20 cm. Its area would be:
Area = (1/2)
- d1
- d2 = (1/2)
- 15 cm
- 20 cm = 150 cm2
Additional Considerations
When calculating the area of kites, certain special cases and exceptions arise that require specific attention.
Additionally, there are variations and extensions of the concept of a kite that introduce new considerations in area calculation.
Special Cases
In some instances, the diagonals of a kite may not be perpendicular to each other, resulting in an oblique kite. The area formula for oblique kites requires the use of trigonometry to account for the angle between the diagonals.
Variations and Extensions
The concept of a kite can be extended to include kites with curved edges or kites with additional interior angles. These variations may require more complex formulas or techniques for calculating the area.
FAQ Insights
What is the formula for finding the area of a kite?
The area of a kite is given by the formula: Area = (1/2) – (d1 – d2), where d1 and d2 represent the lengths of the diagonals.
How do I find the diagonals of a kite?
There are several methods to find the diagonals of a kite, including using the Pythagorean theorem, applying geometric relationships, or measuring them directly.
What are some special cases or exceptions in calculating the area of kites?
Special cases may arise when the kite is a rectangle, square, or parallelogram, where different formulas or properties may apply.